Headings and Structure
Organizing content with clear headings and a logical structure is essential for creating accessible digital content. Proper use of headings allows all users to quickly understand how information is organized and easily access the content.
Why Headings Matter
Well-structured headings offer many benefits to users, namely:
- Improved Navigation: Assistive technologies, such as screen readers, rely on headings to help users quickly locate and understand content sections.
- Enhanced Comprehension: Organized content keeps readers focused and reduces frustration, improving their overall experience. Clear headings break content into digestible sections, aiding all users in understanding and retaining information.
It is not enough to use font size or styling to organize your content as screen readers and other assistive technology do not recognize this formatting. Using proper heading formats will ensure access for all users.
How To
General Practice
Review Your Content. Scan your page to identify its main sections.
Think Hierarchically. Begin with one heading level 1 (H1) for the title only, then apply heading level 2’s (H2’s) for major sections, H3’s for subsections, and so on.
Ensure logical flow. For example, do not skip from H1 to H4.
Be Descriptive. Headings should clearly summarize the content of the section.
Keep It Simple. Avoid overly long or complex headings.
Check Accessibility. Use tools like the built-in accessibility checker for Microsoft applications or the WAVE browser extension for webpages to test the structure of your headings and edit as needed.
Technical Tips
Use Proper HTML Tags. Use <h1> for the main title, <h2> for subheadings, and so on, maintaining a logical order.
Headings should only be used to organize content. Use CSS for visual design.
What to Avoid
- Skipping Levels: Avoid jumping from an
<h1>to an<h3>without an<h2>in between. - Using Headings for Styling: Do not use headings solely for visual styling (e.g., to make text appear larger or bolder); they should convey structural meaning so as not to mislead users.
- Quick tip: In MS Word, you have the ability to customize heading styles if you do not like the default stylization. Visit Creating Accessible MS Word Documents for a video demo on how to customize heading styles while retaining heading structure.
- Non-Descriptive Text: Avoid vague headings like “Click Here” or “More Info.”
- Empty Headings: Ensure every heading is paired with meaningful content.
Examples
Applying Headings on Webpages
For this very webpage, “Headings” is the title of the page and the sole heading level 1 (H1). The major sections (“Headings and Structure,” “Why Headings Matter,” “How To,” etc.) are structured as H2’s with the subsections, “General Practice” and “Technical Tips,” nested under “How To” as H3’s. (The following applies to WordPress, but other tools offer similar methods.)
Step 1: Focus on your text and locate the toolbar that appears adjacent to it.
Step 2: Locate and select the Paragraph (“P”) button to expand the “Transform To” drop-down menu. Select Heading.
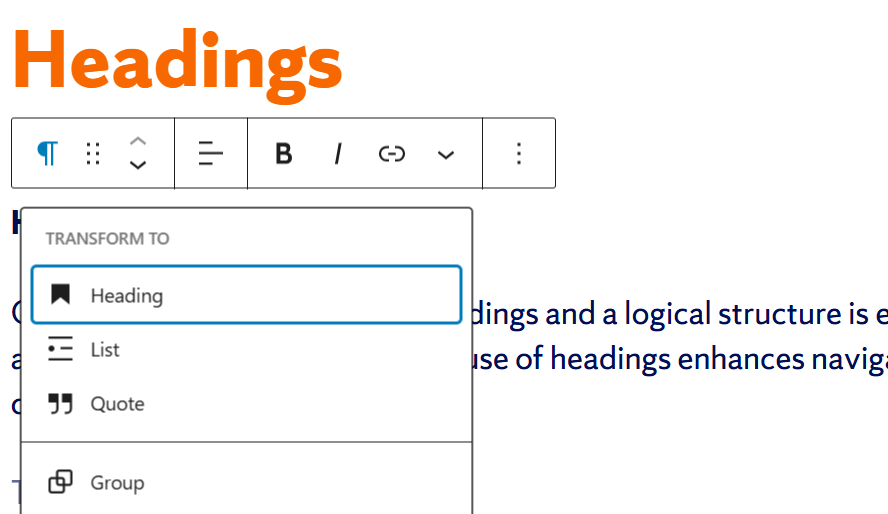
Step 3: Choose the appropriate heading level from the headings drop-down menu.

Applying Headings in Microsoft Word
For a video demonstration on applying headings in MS Word, please visit our page on Creating Accessible MS Word Documents.
Additional Resources
Ally is an excellent course accessibility evaluation tool available to instructors within Blackboard Ultra. Always check the “How to…” guidance within your Blackboard Ultra course and visit Using Ally in Blackboard Ultra for more information. Additional guidance provided by Ally is as follows:
When scanning a webpage using the WAVE web accessibility evaluation tool, you may encounter errors or alerts, indicating accessibility barriers. Pope Tech offers the following guidance on addressing these issues:
Errors
